202 Tutotail - 5
Q1: Explain addressing modees and also explain what is effective address ?
Ans :
Adressing Modes
The operation field of an instruction specifies the operation to be performed. This operation will be executed on some data which is stored in computer registers or the main memory. The way any operand is selected during the program execution is dependent on the addressing mode of the instruction. The purpose of using addressing modes is as follows:
- To give the programming versatility to the user.
- To reduce the number of bits in addressing field of instruction.
Types of Addressing Modes:
Immediate Mode
In this mode, the operand is specified in the instruction itself. An immediate mode instruction has an operand field rather than the address field.
For example:
ADD 7, which says Add 7 to contents of accumulator. 7 is the operand here.Register Mode
In this mode the operand is stored in the register and this register is present in CPU. The instruction has the address of the Register where the operand is stored.
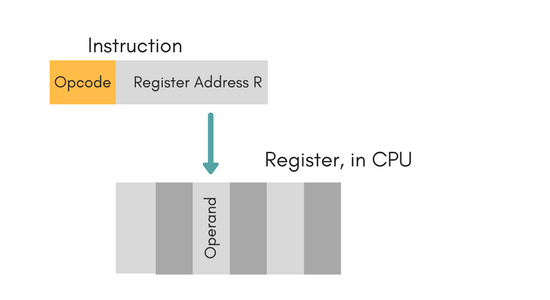
Advantages of this mode:
- Shorter instructions and faster instruction fetch.
- Faster memory access to the operand(s)
Disadvantages of this mode:
- Very limited address space
- Using multiple registers helps performance but it complicates the instructions.
Register Indirect Mode
In this mode, the instruction specifies the register whose contents give us the address of operand which is in memory. Thus, the register contains the address of operand rather than the operand itself.
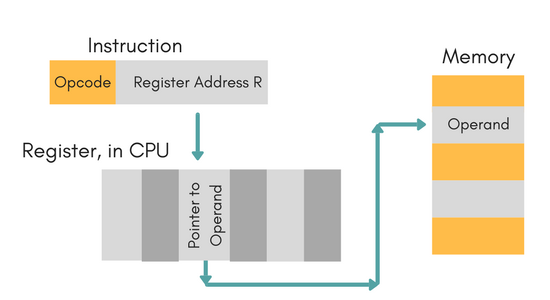
Auto Increment/Decrement Mode
In this the register is incremented or decremented after or before its value is used.
Direct Addressing Mode
In this mode, effective address of operand is present in instruction itself.
- Single memory reference to access data.
- No additional calculations to find the effective address of the operand.
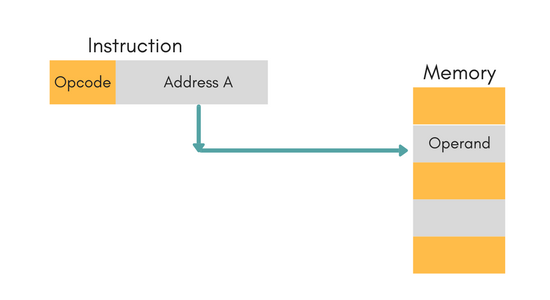
For Example:
ADD R1, 4000 - In this the 4000 is effective address of operand.
NOTE: Effective Address is the location where operand is present.
Indirect Addressing Mode
In this, the address field of instruction gives the address where the effective address is stored in memory. This slows down the execution, as this includes multiple memory lookups to find the operand.
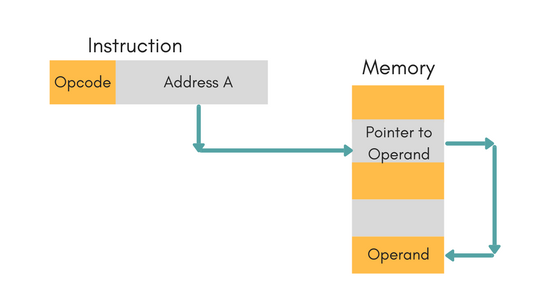
Displacement Addressing Mode
In this the contents of the indexed register is added to the Address part of the instruction, to obtain the effective address of operand.
EA = A + (R), In this the address field holds two values, A(which is the base value) and R(that holds the displacement), or vice versa.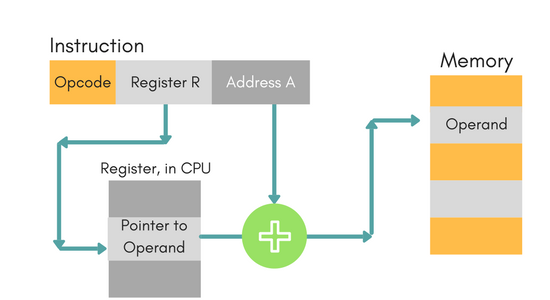
Relative Addressing Mode
It is a version of Displacement addressing mode.
In this the contents of PC(Program Counter) is added to address part of instruction to obtain the effective address.
EA = A + (PC), where EA is effective address and PC is program counter.
The operand is A cells away from the current cell(the one pointed to by PC)
Base Register Addressing Mode
It is again a version of Displacement addressing mode. This can be defined as
EA = A + (R), where A is displacement and R holds pointer to base address.Stack Addressing Mode
In this mode, operand is at the top of the stack. For example:
ADD, this instruction will POP top two items from the stack, add them, and will then PUSH the result to the top of the stack.
Q2 :


202 Tutotail - 5 - Computer Keda >>>>> Download Now
ReplyDelete>>>>> Download Full
202 Tutotail - 5 - Computer Keda >>>>> Download LINK
>>>>> Download Now
202 Tutotail - 5 - Computer Keda >>>>> Download Full
>>>>> Download LINK